A fuse protects electrical appliances and equipment by breaking the electrical circuit in the event of an overload of current or a short circuit. There are a number of different types of fuses available, and these differ in size, shape and material. When a fault occurs, such as an overload or short circuit, the high current that is flowing through the fuse melts the fuse element, thus interrupting the flow of current and breaking the circuit. This prevents the appliance from damage due to excess current.
Each fuse responds differently to current flow and surges, and takes a different amount of time to react; it is therefore important to choose the correct fuse for the circuit it is to be introduced in. An incorrect fuse could either mean no protection because it has not melted in time, or over sensitivity when it blows repeatedly for no real reason.
KT Ranges a large variety of Fuses including:
- Ceramic Fuses
- Glass Fuses
- Micro Blade Fuses
- Mini Blade Fuses
- Standard Blade Fuses
- Maxi Blade Fuses
Click Here to View KT’s Fuse & Fuse Holders Catalogue Section
What Are KT Fuses Made From?
KT Fuses are made from Glass, Ceramic, or Plastic. The body of a Glass Fuse is called the barrel and it has a terminal made of plated copper or brass at each end. These terminals are connected by the fuse element, which is made of copper, aluminium, zinc, or silver. The element could either be a single wire, or consist of more than one wire. The multiple wires could be arranged in different ways to make the fuse behave differently. Sometimes, sand or quartz powder is filled in the body to alter the behavior of the fuse. This is usually the case in a ceramic fuse.
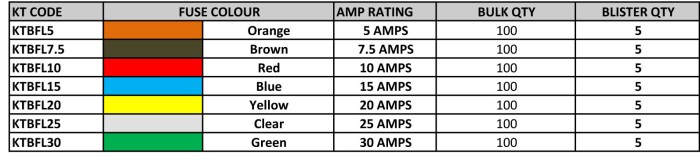
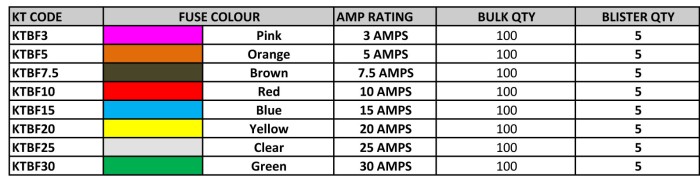
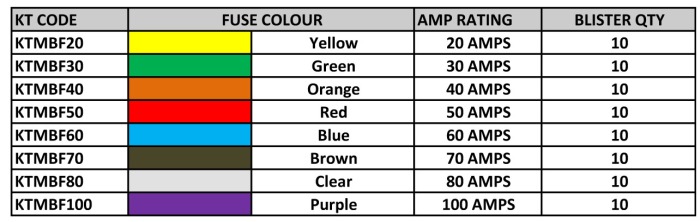
Blade fuses (also called spade or plug-in fuses), with a plastic body and two prongs that fit into sockets, are mostly used in the Automotive Industry. Each fuse is printed with the Rated Current in Amperages on the top. Standard Fuses were developed in 1976 for low-voltages use in motor vehicles. The Mini Blade Fuses were developed in the 1990’s. Blade Fuses can be mounted in fuse blocks, in-line fuse holders, or fuse clips. KT Blade Fuses are available in Micro, Mini, Standard and Maxi Sizes.
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
Glass and Ceramic Fuses are often used to protect appliances and consumer electronics. As electronic equipment becomes smaller, the circuits and components become more delicate and easily damaged. Fuses are the preferred method of protection due to their accuracy, small size and reliability. Fuses are available in a wide variety of amp ratings to provide precise protection. Generally, two sizes of user-replaceable fuses are found: the 1/4” x 11/4” and 5 x 20mm. Each is available in a variety of volt and amp ratings. In a glass fuse, the element is visible, and this makes inspection easy, while a ceramic fuse is opaque. A glass fuse has a low breaking or rupturing capacity. What this means is that the fuse element melts when there is a high current or voltage. It is therefore not suitable for appliances and equipment’s that draw a lot of current.
Glass fuses have a low thermal stability and shatter in high-heat conditions. Ceramic fuses, on the other hand, can withstand high temperatures and are more thermally stable.
Ceramic fuses, unlike glass fuses, are also often filled with a filler like sand to prevent the formation of a conductive film. When there is a short circuit, the fuse element melts and vaporizes. It deposits on the inside of the barrel or body as a film. In a glass fuse, the body continues to get heated and the film begins to conduct electricity, thus rendering the fuse inefficient. The sand in a ceramic fuse, however, absorbs the heat energy and prevents the fuse from heating and therefore conducting.
____________________________________________________________________________
Ceramic Fuses were commonly used in the Automotive Industry, however are not as commonly used in today compared with Blade and Glass Fuses. Ceramic Fuses have a high breaking or rupturing capacity and are suitable for high current and voltage circuits. Some ceramic HRC (high rupturing capacity) fuses can safely interrupt up to 300,000 amperes of current, while normal glass fuses have a much lower capacity, sometimes as low as only 15 amperes.
____________________________________________________________________________
How will I know which Fuse is Suitable for My Needs?
It is important to consider the following factors before installing a fuse:
- For electronic/electrical applications, fuse must be rated at 125V or better.
- Voltage must match or exceed the fuse being replaced (125V for household current; 12V for auto; 24V for heavy duty).
- Fuse must match required fuse characteristic – either fast-acting or time-delay.
- Amp rating must match that of the original fuse.
The maximum continuous current rating, which indicates the maximum current that can pass through a fuse; the rupturing or breaking capacity, which indicates the maximum current that can be interrupted without causing damage; the voltage rating–the fuse must be used at less than the rated voltage. Ensure you choose the right fuse for your appliances and equipment to protect them and to reduce the risk of overheating and fire. If you are unsure, speak to an electrician.
All fuses have a voltage rating. To maintain safety, this voltage rating should not be exceeded in application, although it is acceptable to use a higher rated fuse in a lower voltage application. For example: A fuse rated for 125 volts is appropriate in household (110V) or Automotive (12V), while a fuse rated for 32 volts is appropriate for automotive (12V), but not for household (125V). Always replace a fuse with one of the same or higher voltage rating.